

| HOME |
ABOUT |
FACILITIES EXPERTISE |
VANADIUM PROCESSING |
ZERO CARBON IRON MAKING |
TANTALUM TUNGSTEN |
VANADIUM ELECTROLYTE |
RARE
EARTH RECYCLING |
ELECTRODES |
ELECTROLYZERS |
PATENTS |
NEWS |
LINKS |
CONTACT |
 Français Français |
 |
BOOKS CATALOG |
SPRING 2025 Imprint: Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc., Montréal, Canada ISNI: 0000 0005 1247 3654 Heavy Liquids for the Separation of Minerals: Their Preparation, Properties, and Uses. by François Cardarelli, 545 pages, 285 tables, 76 figures. Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc., 2025. ISBN 978-1-7775769-6-7 Softcover | ISBN 978-1-7775769-8-1 Hardcover | ISBN 978‐1‐7775769‐7‐4 eBook Google Play | Amazon.com Electrowinning iron and recycling sulfuric acid from iron sulfates: a zero-carbon iron-making process. by François Cardarelli, 499 pages, 181 tables, 140 figures, Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc., 2023. ISBN 978-1-7775769-3-6 Softcover | ISBN 978-1-7775769-5-0 Hardcover | ISBN 978‐1‐7775769-4-3 eBook Google Play | Amazon.com Sulfuric acid digestion, sulfuric acid baking, and sulfation roasting in mineral and chemical processing, and extractive metallurgy. by François Cardarelli; 309 pages, 93 tables, 76 figures; Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc., 2022. ISBN 978-1-7775769-0-5 Softcover | ISBN 978-1-7775769-2-9 Hardcover | ISBN 978‐1‐7775769‐1‐2 eBook Google Play |
 |
March 24, 2025 - BOOK | Heavy Liquids for the Separation of
Minerals: Their Preparation, Properties, and Uses
Heavy Liquids for the Separation of Minerals: Their Preparation, Properties, and Uses. by François Cardarelli, 545 pages, 285 tables, 76 figures. Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc., 2025. ISBN 978-1-7775769-6-7 Softcover | ISBN 978-1-7775769-8-1 Hardcover | ISBN 978‐1‐7775769‐7‐4 eBook Available from these booksellers: Google Play | Amazon.com Flyer (Front Cover - Table of Contents - List of Figures - List of Tables - Index - About the Author - Back Cover) This
monograph is primarily intended to describe the main physical
and
chemical properties of heavy organic liquids (e.g., bromoform, tetrabromoethane, diiodomethane), dense aqueous
solutions of
salts of inorganic acids
(e.g., halides, sulfates, nitrates, perchlorates, molybdates,
tungstates, metatungstates, polytungstates, polyoxometalates,
tantalates, perrhenates, etc.), and salts of organic acids (e.g, formates, acetates, oxalates, malonates, benzoates, salicylates, citrates, etc.) and heavy suspensions used in mineralogy, gemology, mining, metallurgy, and chemistry for the separation by gravity of minerals, metallic ores,
graphite, coal
macerals, fossils, diamonds and gemstones along with plastics, glass, ceramics
and
other synthetic materials. Moreover dense solutions of cesium and rubidium salts used in
biology
for the separation of nucleic acids, and other biological molecules of
interest
by centrifugation using density gradients are also described. For several heavy liquids, it provides a detailed description of the laboratory methods, and industrial processes utilized for their preparation along with the most efficient recovery and recycling techniques. Moreover, when available the occupational health and safety information for toxic and hazardous chemicals used as heavy liquids is also provided to ensure safe practices in the work place.
|
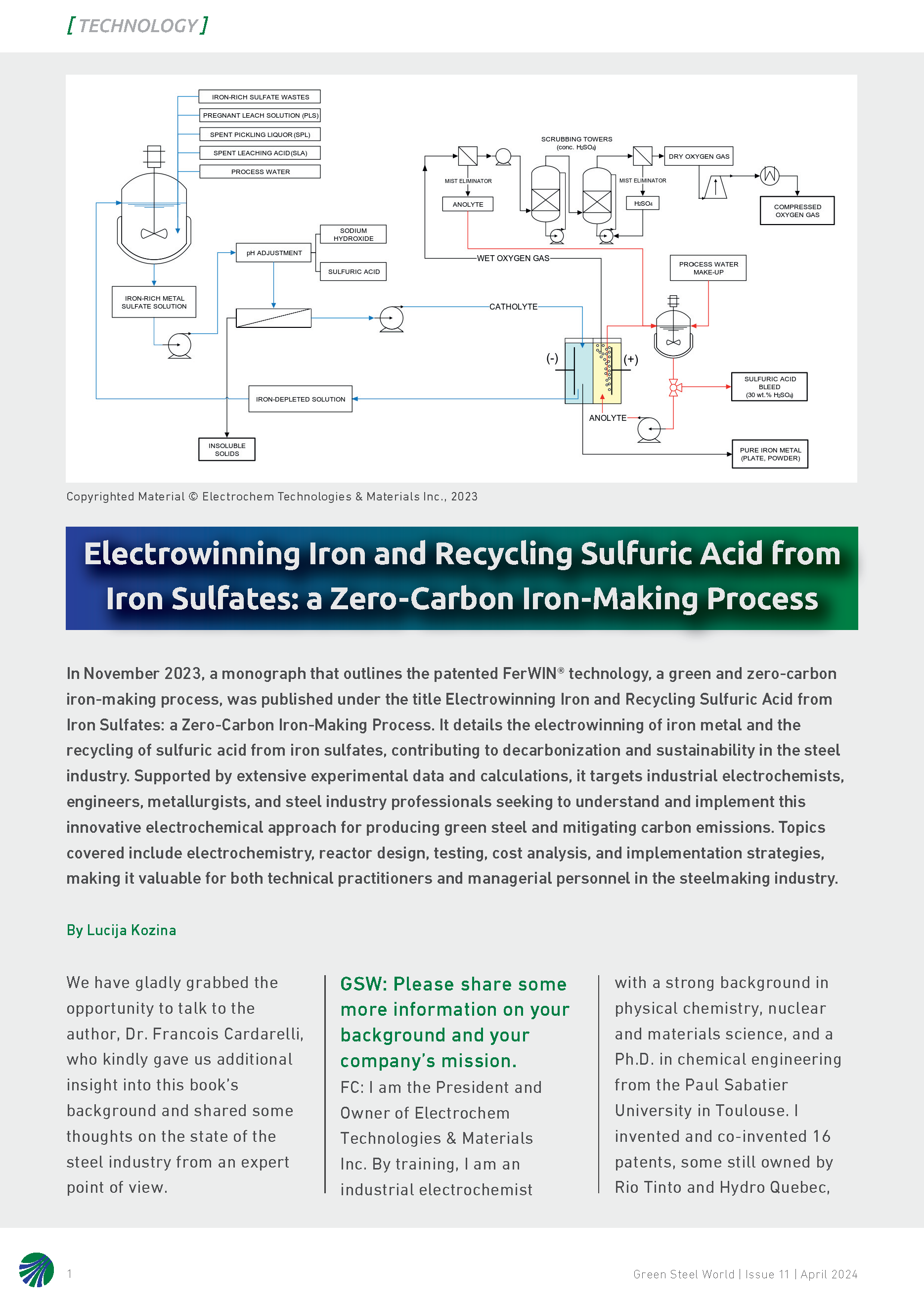 |
April 20, 2024 - Review of the book "Electrowinning Iron and Recycling Sulfuric Acid from Iron Sulfates: a Zero-Carbon Iron-Making Process" was Published in Green Steel World Montreal, QC - April 20th, 2024, Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. is pleased to announce that
the 499-page book entitled: “Electrowinning Iron and Recycling Sulfuric
Acid from Iron Sulfates: a Zero-Carbon Iron-Making Process” authored by François Cardarelli that
describes the scientific, technical, and economic aspects of the
patented FerWIN® process was featured by Lucija Kozina, Editor of the
Global online magazine Green Steel World in the April 2024 issue pages 20-22 [PDF file (189 KB)].
|
 |
November 27, 2023 - BOOK | Electrowinning Iron and Recycling Sulfuric Acid from Iron Sulfates: a Zero-Carbon Iron-Making ProcessElectrowinning iron and recycling sulfuric acid from iron sulfates: a zero-carbon iron-making process. by François Cardarelli, 499 pages, 181 tables, 140 figures, Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc., 2023. ISBN 978-1-7775769-3-6 Softcover | ISBN 978-1-7775769-5-0 Hardcover | ISBN 978‐1‐7775769-4-3 eBook Available from these booksellers: Google Play | Amazon.com Flyer (Front Cover - Table of Contents - List of Figures - List of Tables - Index - About the Author - Back Cover) This
comprehensive monograph is primarily intended to
describe the patented FerWIN® technology, a green and zero-carbon
iron-making
process, which consists to perform the electrowinning of iron metal and
the
recycling of sulfuric acid from iron sulfates that are by-produced at
the
million tons scale worldwide while releasing pure oxygen gas off
setting greenhouse gases and contributing to the decarbonization of the
steel industry towards sustainability and a circular economy. The
information has been presented in such a form that
industrial electrochemists, chemical engineers, metallurgists, and
other
practicing engineers, scientists, professors, and technologists will
have
access to relevant scientific and technical information supported by
key
experimental data that were obtained from more than a decade of
extensive laboratory,
prototype, and
pilot testing at company facilities and client locations. It also
includes comprehensive electrochemical and
engineering
calculations, costs and benefits analysis, financial and sensitivity
analysis for an iron electrowinning plant with a
nameplate capacity of
100,000 tonnes of pure iron metal per year. This
monograph will be of value also to men and women
engaged in the traditional iron and steelmaking industries that want to
understand this novel electrochemical technology outside their
conventional
blast furnace, direct reduced iron, and electric arc smelting processes
to produce green steel and to avoid carbon emissions, and
the associated risks of using hydrogen gas. Finally,
the monograph may be of interest to persons
in the steelmaking industries occupying managerial positions such as
chief
executives, chief operating officers, and V.P. of operations. |
April
20th, 2023 - PCT OF THE INTERNATIONAL PATENT APPLICATION WO 2023/060337
(A1) PUBLISHED BY THE WIPO
MONTREAL,
QC – April 20th, 2023, The World
Intellectual Property Organization (www.WIPO.int)
has just published the PCT of the International Patent Application WO
2023/060337 (A1)
[PDF file (491 KB)] entitled HIGH
TEMPERATURE CHEMICAL PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF CESIUM TUNGSTATE
(Inventor: François
CARDARELLI) The present
disclosure broadly relates to a high temperature chemical process for
the synthesis of cesium tungstate in the solid state and the
preparation of aqueous solutions or deuterated solutions of cesium
tungstate. More specifically, but not exclusively, the present
disclosure relates to a high temperature chemical process in which
tungsten oxide compounds such as tungsten oxides, or natural or
synthetic concentrates such as wolframite or scheelite, tungsten
industrial by-products or their mixture thereof, are mixed with cesium
compounds such as cesium carbonate, or cesium sulfate, or cesium
hydroxide or their mixtures thereof and the mixture is roasted in air
or oxygen at high temperature inside a kiln. After cooling, the solid
sintered mass containing cesium tungstate is leached or dissolved with
water or heavy water for producing dense aqueous solutions or
deuterated solutions of cesium tungstate |
|
 |
December 17, 2022 - BOOK |
Sulfuric Acid Digestion, Sulfuric Acid
Baking, and Sulfation Roasting in Mineral and Chemical Processing, and
Extractive Metallurgy
Sulfuric acid digestion, sulfuric acid baking, and sulfation roasting in mineral and chemical processing, and extractive metallurgy. by François Cardarelli; 309 pages, 93 tables, 76 figures; Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc., 2022. ISBN 978-1-7775769-0-5 Softcover | ISBN 978-1-7775769-2-9 Hardcover | ISBN 978‐1‐7775769‐1‐2 eBook Available from these booksellers: Google Play Flyer (Front Cover - Table of Contents - List of Figures - List of Tables - Index - About the Author - Back Cover) This monograph is primarily intended to serve as a concise review of the industrial utilization of sulfuric acid and the plethora of sulfation techniques used extensively in the mineral, chemical, and metallurgical industries across the world. The information has been presented in such a form that industrial chemists, chemical engineers, and other practicing engineers, scientists, professors, and technologists will have access to relevant scientific and technical information supported by key data gathered from several disseminated sources along with a brief description of each major industrial processes (e.g., phosphates, titanium dioxide, lithium, alumina, and beryllium), and finally several novel sulfation technologies that might be implemented in the near future. This monograph will be of value also to men and women engaged in other branches of chemistry and metallurgy that want to understand these techniques outside their field of expertise. Finally, the monograph may be of interest to persons in the chemical and metal industries occupying nontechnical positions such as executives, patent attorneys, traders, purchasing agents, salesmen and women, to whom a general knowledge of the technical aspect of their business would be helpful. |
 |
October
13th, 2022 - PCT OF THE INTERNATIONAL PATENT APPLICATION WO 2022/213173
(A1) PUBLISHED BY THE WIPO
MONTREAL,
QC – October 13th, 2022, The World
Intellectual Property Organization (www.WIPO.int)
has just published the PCT of the International Patent Application WO
2022/213173 (A1)
[PDF file (3.29 MB)] entitled ELECTROCHEMICAL
PREPARATION OF VANADIUM ELECTROLYTES AND SULFATES OF MULTIVALENT
TRANSITION METALS. (Inventor:
François CARDARELLI) This novel electrochemical process addresses the
preparation aqueous solutions of vanadium sulfates or aqueous solutions
of transition metal sulfates and the recycling of end-of-life (E-o-L)
vanadium electrolytes. More specifically, but not exclusively,
the present disclosure relates to a direct electrochemical process in
which a suspension, obtained by slurrying transition metals oxides such
as oxides of vanadium, oxides of iron, oxides of cobalt, oxides of
nickel, oxides of chromium, oxides of manganese, oxides of titanium,
oxides of cerium, oxides of praseodymium, oxides of europium, oxides of
terbium, oxides of uranium, oxides of plutonium, or their mixtures
thereof with sulfuric acid as carrier fluid, is reduced
electrochemically inside the cathode compartment of an electrolyzer to
produce an aqueous solution of vanadium sulfates or of transition metal
sulfates. Simultaneously, concentrated sulfuric acid and oxidizing
co-products such as oxygen gas, peroxodisulfuric acid (H2S2O8),
ammonium persulfate [(NH4)2S2O8],
chromic acid (H2CrO4), cerium (IV) sulfate
[Ce(SO4)2],
manganese dioxide (MnO2), and vanadium pentoxide (V2O5)
from spent vanadium electrolyte can be produced inside
the anode compartment. |
 |
June 1st, 2022 - Recycling BAUXITE RESIDUES AND electrowinning ELECTROLTYTIC ironNEW YORK CITY, NY – June 1st, 2022 – The American trade magazine CHEMICAL ENGINEERING MAGAZINE (https://www.chemengonline.com) has just published its June 2022 issue including a press release describing the novel electrochemical process and entitled - "Recycling Bauxite Residues and Electrowinning Iron." - written by Gerald Ondrey. The article is published in the Chementator section on page 9. |
 |
April
14th, 2022 - Recycling BAUXITE RESIDUES
AND electrowinning ELECTROLTYTIC iron
MONTREAL, QC – April
14th, 2022 -
Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc.
(www.electrochem-technologies.com) produced pure electrolytic iron
(99.995% Fe) using its patented FerWIN™ process, a sustainable
zero-carbon iron-making technology, from ferrous sulfate heptahydrate
(copperas) originating from the sulfation of bauxite residues. This
pilot test work completes the prior piloting campaign that was
conducted in 2016 with bauxite residues, red mud and spent solutions
from an alumina refinery. The process consists to react concentrated
sulfuric acid with bauxite residues from which iron, aluminum, and
sodium sulfates along with gypsum are recovered. Then the
electrowinning of iron metal was performed on the crystallized
copperas. Pure electrolytic iron flakes were electrowon inside a
rectangular electrolyser with 10 square feet of cathodes while
regenerating the concentrated sulfuric acid to be recycled upstream
during sulfation. Based on the excellent faradic current efficiency
(98%), throughput and low specific energy consumption (2.9 kWh/kg Fe),
we are optimistic that combining the sulfation of bauxite residues and
the electrowinning of iron could represent a possible route for
neutralizing, dewatering, recycling and valorizing red mud and bauxite
residues. This is particularly true in locations having an oversupply
of sulfuric acid from nearby smelters and affordable nuclear- or hydroelectricity.
From an environmental standpoint, the FerWIN™ process also releases
pure oxygen gas to the atmosphere generating carbon tax credits. As the
patented technology is now granted and enforced in 16 key jurisdictions
(Canada, China, Japan, South Africa, Europe, Brazil, and India) where
red mud landfills represents a serious environmental hazard, the
company is seeking to secure licensing agreements of the FerWIN™
process worldwide. where red mud #landfills represents a serious
environmental hazard. As the technology is now technically proven,
de-risked, and the costs and benefits analysis favorable, the company
is currently seeking to secure licensing agreements for the FerWIN™
process with industrial partners across the aluminum industry. The
company is in discussion with alumina producers in three jurisdictions
but it is also seeking to enter into wider licensing agreements of the
FerWIN™ process worldwide as the company wishes to remain focused on
its commercial production of vanadium, tantalum, tungsten chemicals,
and industrial electrodes while benefiting from royalties. |
 |
February 1st,
2022 - AN ELECTROCHEMICAL PROCESS FOR PRODUCING AND RECYCLING VRFB
ELECTROLYTES
NEW
YORK CITY, NY – February
1st, 2022 – The
American trade magazine CHEMICAL
ENGINEERING MAGAZINE (https://www.chemengonline.com)
has just published its February 2022 issue including a press release
describing the novel electrochemical process and entitled - "An
electrochemical process for producing and recycling VRFB electrolytes." - written by Gerald
Ondrey. The article is published in the Chementator section on page 6. The PCT of the
International Patent Application of the process is WO
2022/213173 (A1)
[PDF file (3.29 MB)] |
 |
October 15th, 2021 - COMMERCIAL PRODUCTION OF TANTALUM, NIOBIUM, and TUNGSTEN in QUEBEC (CANADA)MONTREAL, QC – August 20th, 2021 - Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. produces commercially tantalum, niobium and tungsten by performing the chemical processing and recycling of natural and synthetic concentrates, by-products of tantalum, niobium, tin, and tungsten such as tungsten carbide sludge, scrapmetal metal, cermets, and hardmetal, the company reached this year an inventory totalizing 2,500 lb. of pure tantalum, niobium, and tungsten chemicals such as Tantalum (V) Oxide (Ta2O5), Niobium (V) Oxide (Nb2O5), Tungsten (VI) Oxide (WO3) and Cesium Tungstate (Cs2WO4). The patented and ecofriendly process (Canadian Patent CA 2,849,787 C) consists to perform the caustic fusion followed by hot alkaline leaching. Afterwards, tantalum and niobium are separated from tungsten by selective precipitation as hydrated sodium hexatantalate (Na8Ta6O19.9H2O) and sodium hexaniobate (Na8Nb6O19.9H2O) that are hot acid leached (HAL) and then recovered by calcining as pure tantalum pentoxide and niobium pentoxide. The tungsten values are entirely recovered as Hydrated Tungstic Acid (H2WO4.H2O) which is converted to Blue Tungsten Oxide (BTO), Yellow Tungsten (VI) Oxide (YTO), Cesium Tungstate (Cs2WO4) for heavy media separation, and tungsten bronzes such Tantalum Tungsten Oxides (Ta2WO8) and Niobium Tungsten Oxides (NTOs) with chemical formulae Nb16W5O55 and Nb18W16O93 used as novel battery materials. These fine chemicals are sold to key customers. Because the chemical process does not relies on the utilization of hazardous hydrofluoric acid (HF) and noxious solvent extraction (SX) it is safer from an occupational safety standpoint. Moreover all the liquid effluents are recycled by causticizing and thermal evaporation that makes it a greentechnology compared with the conventional route. The company current inventory of tantalum, niobium, tungsten, and cesium chemicals together with vanadium electrolyte for VRFB and vanadium chemicals, puts the company in an excellent commercial position for the production of these raremetals and high-priced critical metals and strategic materials in Quebec and in Canada. For tolling agreements, commercial inquiries, supply of raw materials, and pricing please contact us. |
 |
August 20th, 2021 - VANADIUM ELECTROLYTE PRODUCTION COMMERCIAL DEPLOYMENTMONTREAL, QC – August 20th, 2021 - Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. operates commercially several electrochemical units for the sustainable production and recycling of vanadium electrolytes using its proprietary and patent pending electrochemical technology. Recently, negotiations with end-users started for acquiring modular skid-mounted or containerized units with production capacities ranging from 5,000 L to 25,000 L per day. These units will be either sold or used under license. Discussions with several engineering companies and constructors are ongoing to select the most suited partners for the commercial deployment. This integrated approach to process on-site vanadium raw materials, and to produce directly proprietary Vanalyte™ and SuperVanalyte™ formulations at clients locations seems attractive for several end users. These units are also capable for balancing vanadium electrolytes and to recover efficiently vanadium values as vanadyl sulfate or vanadium pentoxide both suitable to be reused as precursors or sold as chemicals. Negotiations continues also with primary vanadium producers and vanadium redox flow battery VRFB manufacturers for establishing a broader strategic partnership for a vertically integrated business model in Canada and abroad. For more information contact us or download our bilingual brochure (http://www.electrochem-technologies.com/PDFs/ELECTROCHEM_VANADIUM_ELECTROLYTE_BROCHURE_2021_EN_FR.pdf). |
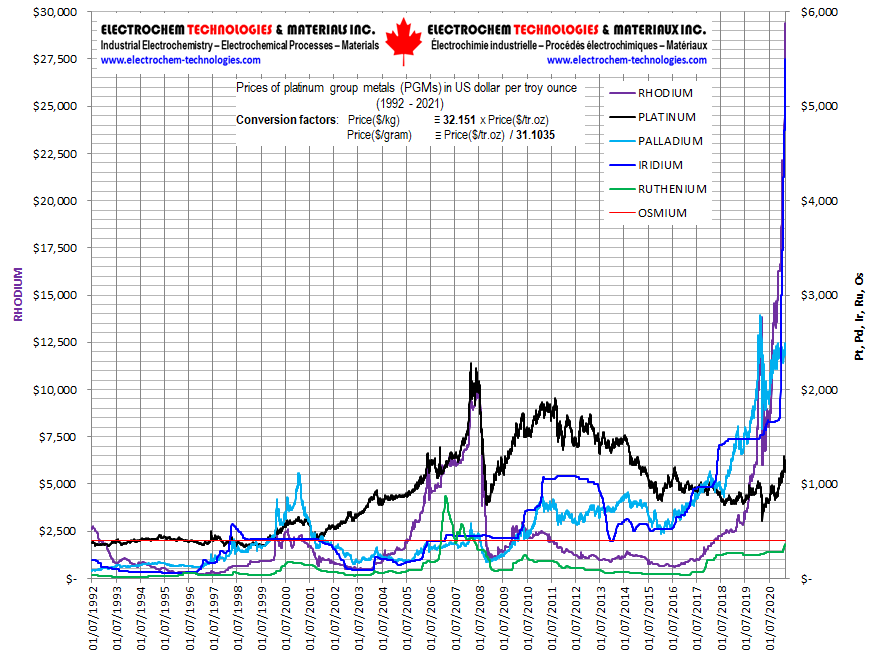 |
March 23rd,
2021 - IS THE ELECTROCHEMICAL INDUSTRY AT RISK WITH THE SKYROCKETING
PRICES FOR IRIDIUM AND RUTHENIUM METALS?
|
 |
January 30th, 2021 - NEW UNITS FOR THE PRODUCTION AND RECYCLING OF VANADIUM ELECTROLYTEMONTREAL, QC – January 30th, 2021 – Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. build and installed three additional units the production of vanadium electrolyte and the recycling of vanadium electrolyte from end-of-life and spent vanadium electrolytes. This bring the total of six production units. The qualification and testing of the new units have been completed and they are ready for use. This significantly increases the company's combined and integrated capabilities in Canada to process vanadium-rich feedstocks and raw materials, to produce our proprietary vanadium electrolyte (Vanalyte™ and SuperVanalyte™) and to recycle vanadium electrolytes. As for the previous units they are also capable to re-balance spent electrolyte and to recover vanadium values from the spent vanadium electrolytes as vanadyl sulfate heptahydrate or high purity vanadium pentoxide both suitable to be reused as new precursors or as fine chemicals. Commercially, the company continues negotiations with established vanadium producers and vanadium redox flow battery manufacturers for establishing a key strategic partnership for a large vertically integrated business model in Canada. For more information contact us or download our bilingual brochure (http://www.electrochem-technologies.com/PDFs/ELECTROCHEM_VANADIUM_ELECTROLYTE_BROCHURE_2021_EN_FR.pdf). |
 |
December 17th, 2020 - DISCUSSIONS RESUMED FOR LICENSING THE PATENTED FerWIN PROCESS FOR ELECTROWINNING IRON FROM FERROUS SULFATE, COPPERAS, MINING WASTES, EFFLUENTS, AND SPENT PICKLING LIQUORSMONTREAL, QC – December 17th, 2020 – Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. (“Electrochem”) is pleased to announce that commercial discussions for the licensing of the patented Electrochemical process for the recovery of metallic iron and sulfuric acid values from iron-rich sulfate wastes, mining residues, and pickling liquors in key jurisdictions resumed with industrial partners from Canada, Brazil, India, RSA and the European Union (EU) some of them having already tested the technology. The now called FerWIN™ (i.e., the contraction of Ferrum and ElectroWINning) Process granted and enforced in sixteen countries worldwide is a sustainable zero-carbon iron making technology that produces pure iron and releases oxygen gas instead of carbon dioxide. The low specific energy consumption yields an operating cost particularly competitive where affordable electricity is available especially in Qubec and Scandinavia. Because of the large availability of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas) a by-product from the metallurgical and chemical industries it is a perfect time for integrating the patented technology vertically. As several new prospects were approaching Electrochem recently regarding the patented FerWIN™ process we have prepared a bilingual technical brochure with key figures that will allow other parties to have an excerpt of the technology readily available prior contacting us. |
 |
November 24th, 2020 - VANADIUMCORP RESOURCE INC. PURCHASES PATENT RIGHTS FROM ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. FOR THE VANADIUMCORP-ELECTROCHEM PROCESS TECHNOLOGY (VEPT)MONTREAL, QC – November
24th, 2020 – Electrochem
Technologies & Materials Inc.
(“Electrochem”) is pleased to
announce that VanadiumCorp
Resource Inc. ("VRB") has purchased pursuant a
patent purchase agreement (PPA) all intellectual property rights for
the VanadiumCorp-Electrochem
Process Technology (VEPT) entitled Metallurgical
and Chemical Process for Recovering of Vanadium and Iron Values from
Vanadiferous Titano-magnetite. This milestone will accelerate the
commercial development in Quebec and abroad of the technology invented
by Dr. Francois Cardarelli. Under an
original agreement with Electrochem, VanadiumCorp had the option to
purchase the 50% remaining interest in the VEPT. Pursuant to the
completed PPA, Electrochem has assigned its interest in the technology
to VRB under the following terms: 1.
Electrochem
has received a cash payment of $350,000.00 CAD. Electrochem will also
be entitled to royalties on production equivalent to three-percent
(3.0%) for every plant using the VEPT worldwide. VanadiumCorp will have
the option to buy-back each one-half percent (0.5%) for one million US
dollars ($1,000,000 USD) up to the full three percent (3.0%) for six
million US dollars ($6,000,000 USD). 2.
Electrochem
will remain the exclusive contractor/consultant for the continued
development of VEPT subject to standard work agreements, budgets and
approvals. 3.
Electrochem
will undertake test work for other companies wishing to utilize the
VEPT process, provided the other companies understand that licensing
will ultimately be required and negotiated, on reasonable terms, with
VanadiumCorp. VanadiumCorp now owns
100% of VEPT Patent Rights and Intellectual Property Portfolio for all
patent applications is key jurisdictions (Canada, USA, EU, Australia,
India, and RSA) Electrochem
is pleased about this outcome and will continue to work with VanadiumCorp. This
milestone demonstrates the strength of our company who owns a portfolio
of 18 patented electrochemical and metallurgical processes granted and
enforced in 16 countries. These green technologies address the
reduction of carbon emission, the circular economy and the recycling of
critical metals. |
 |
July 1st, 2020 - VANADIUM ELECTROLYTE PRODUCTION AND RECYCLING OF VANADIUM ELECTROLYTE RESUME IN CANADAMONTREAL, QC – July 1st, 2020 – Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. is pleased to announce that after the lockdown imposed by the Federal Government of Canada at our production facilities located in Boucherville (QC) due the COVID-19 pandemic, the company was authorized on July 1st to access its facilities and hence has restarted the production of vanadium electrolyte in order to supply vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) end-users. The company also resumed its activities regarding the reprocessing and recycling of vanadium electrolyte from end-of-life and spent vanadium electrolytes. Both operations require the qualification and testing of the vanadium electrolyte with our custom built laboratory and prototype vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) setups that were installed before the lockdown. Our combined and integrated capabilities to process vanadium-rich feedstocks and raw materials, to produce vanadium electrolyte (Vanalyte™ and SuperVanalyte™) and to recycle vanadium electrolytes from spent and end-of-life VRFB batteries and to test our own products with custom built VRFBs is rather unique in Canada. The recycling project itself is part of our in-house R&D program aiming to secure the recycling and to develop new purification techniques. So far the piloting campaigns performed before March allowed us to produce fresh and balanced vanadium electrolyte ready to be reused inside a VRFB. However, we were also able to recover vanadium values from the spent vanadium electrolytes as vanadyl sulfate heptahydrate or high purity vanadium pentoxide both suitable to be reused as new precursors. Commercially, the company will also resume negotiations with established vanadium producers and vanadium redox flow battery manufacturers for securing additional V2O5 units and for establishing strategic partnerships for a fullly integrated business model in Canada and abroad. |
 |
March 15th, 2020 - VANADIUM ELECTROLYTE PRODUCTION AND RECYCLING OF VANADIUM ELECTROLYTE IN CANADA - STATUS OF MID-MARCH 2020MONTREAL, QC – March 15th, 2020 – Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. is pleased to announce that several milestones have been reached for the production of vanadium electrolyte in Quebec (Canada) in order to supply vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB). Our nameplate capacity has been strengthen by the installation of several larger electrolysers. The production of highly concentrated vanadium electrolyte (SuperVanalyte™) with or without stabilizing additives offers thermally stable formulations suitable for both cold and warm climates and for reducing significantly the handling and shipping costs overseas. Once delivered to the VRFB manufacturer and vanadium electrolyte end-users, the client will perform on-site dilution and final adjustment. Conversely, the testing of the Super Vanalyte as concentrated vanadium electrolyte was initiated following the request made by some end-users to increase the volumetric energy density well above the current adopted value. For that purpose, we have designed and built a 5 kW expandable to 20 kW VRFB battery prototype suitable to cope with high vanadium concentration and related issues occurring inside the anode compartment during charging specifically the precipitation of solids and the biphasic mode of operation (i.e. suspension, slurry). The ongoing recycling campaign of end-of-life and spent vanadium electrolyte has shown very intriguing results regarding the electrochemical behavior of several critical impurities some never been reported. Thus hundred of impurities have been identified and traced back to the source of raw material processed (e.g., vanadium, sulfuric acid, deionized water, solvent extraction), to the degradation products of stack materials (e.g. membranes, frames, electrodes, gaskets), to the construction materials used for storage tanks (e.g., plasticizers, catalysts), to the instrumentation probes and finally to the fluid handling equipment (piping, pumps). The aim is to remove metallic impurities and particulates solids, to destroy organic contaminants, to adjust the chemical composition and to perform the balancing. A separate processing unit was built and will be used to address these specific needs especially to avoid the risk of cross-contamination between fresh and spent batches of vanadium electrolyte.This project is part of our in-house R&D program aiming to explore and develop new purification techniques. Commercially, the company is negotiating with established vanadium producers for securing V2O5 units and for establishing strategic partnerships for a fullly integrated business model. |
 |
December 7th, 2019 - VANADIUM REDOX FLOW BATTERY (VRFB) BUILD FOR IN-HOUSE TESTING OF OUR ALL VANADIUM ELECTROLYTE PRODUCED IN CANADAMONTREAL, QC –December 7th, 2019 – Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. is pleased to announce that a vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) prototype has been designed, constructed and its installation will be completed soon to allow the in-house testing of our proprietary all-vanadium sulfate electrolyte solutions (Vanalyte and Supervanalyte). The customized prototype vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) stack of bipolar confiruration exhibits a minimum one kilowatt power and four kilowatt-hour energy rating expandable to 5 kW and 20 kWh by adding more unit cells and two larger vanadium electrolyte storage tanks. For that task, we have manufactured our proprietary electrode materials in-house, used cheap customized membranes and subcontracted the precision machining of our frames and back-plates to build this bulky prototype making it more cost effective than the commercial units we were planing to purchase overseas for the same purpose. The electrical load for discharging the VRFB stack is one of our several electrolyzers used either for electrowinning or inorganic electrosynthesis. Actually, the direct current suplied by secondary batteries is genuinly smooth compared to the rough DC current supplied by our current AC/DC rectifiers always exhibiting ripples. Having an in-house qualification vanadium redox flow battery unit was critical step as our nameplate production capacity for the vanadium electrolyte solution reaches 685 liters per day approaching our target of one cubic meter per day thanks to the construction and installation off several larger electrolysers in the last two months. The vanadium redox flow battery will be used to qualify and test new batches of vanadium electrolyte compositions. Eventually if reliable and robust enough we will consider in the near future to setup a larger vanadium redox flow battery system capable to supply electricity for our future larger facilities and using our own all-vanadium electrolyte produced in-house. This solution will be commercially viable considering the current low market price for technical grade vanadium pentoxide used as raw material in our process. For more information. |
 |
October 17th, 2019 - NATIONAL ENTRY PHASE IN EUROPE FOR THE VANADIUMCORP-ELECTROCHEM PROCESS TECHNOLOGY (VEPT) PATENT APPLICATIONMONTREAL, QC – October 17th, 2019 – Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. is pleased to announce that the company and VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. jointly filed in the European Union the International Patent Application WO 2018/152628 – METALLURGICAL AND CHEMICAL PROCESS FOR RECOVERING VANADIUM AND IRON VALUES FROM VANADIFEROUS TITANOMAGNETITE AND VANADIFEROUS FEEDSTOCKS. The VEPT is a novel chemical process consisting to digest vanadiferous concentrates into sulfuric acid yielding vanadium pentoxide and sulfate, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas), and titanium hydrolysate with low water and energy consumption vs. the conventional smelting and roasting routes. Suitable vanadium feedstocks are magnetite, hematite, BOF-slags, calcine and other industrial wastes and by-products. Filing in Europe was a mandatory step towards commercialization and complements the recent validation and grant of our patented zero-carbon ironmaking process in the EU strengthening Electrochem unique intellectual property position. Like for the Province of Quebec (Canada), Northern Europe has access to large titano-magnetite deposits, skilled workforce and affordable hydro- and nuclear electricity offering similar advantages for integrating vertically the VEPT with the patented iron electrowinning process. |
 |
September 22nd, 2019 - LATEST DEVELOPMENTS ABOUT VANADIUM ELECTROLYTE PRODUCTION IN CANADAMONTREAL, QC – September 22nd, 2019 – Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. is pleased to announce that significant improvements regarding the production of vanadium electrolyte in Canada and that programs were initiated with vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) manufacturers and energy storage end-users. The production capacity target of 1000L/day should be reached soon with the installation of multiple and larger electrolysers. The company started the production of highly concentrated vanadium electrolyte solutions with thermally stable formulations for warm and cold climate to be adjusted and diluted on-site by clients. This option reduces shipping costs to remote locations. The company also investigated the recycling and reprocessing of end-of-life (E-o-L) vanadium electrolyte solutions and identified unusual impurities that were traced back either to the source of raw material processed or the degradation products of VRFB materials or even to the construction materials used for storage tanks and fluid handling equipment. For that purpose, a separate production unit is used to avoid cross-contamination between fresh and spent electrolyte solutions. A program will be carried-out for several months aiming to establish less stringent specifications regarding the upper threshold of impurities that could be used as a standard if approved by several end-users. From a commercial standpoint, the company is discussing the possibility to establish a distribution network overseas and negotiations are ongoing regarding the possible commercial transfer of the technology if compatible with our Canadian operations. Finally, the vanadium electrolyte leasing model proposed by some interested parties was ruled-out due to serious legal environmental liability issues and future insolvency risks of the lessee. For more information. |
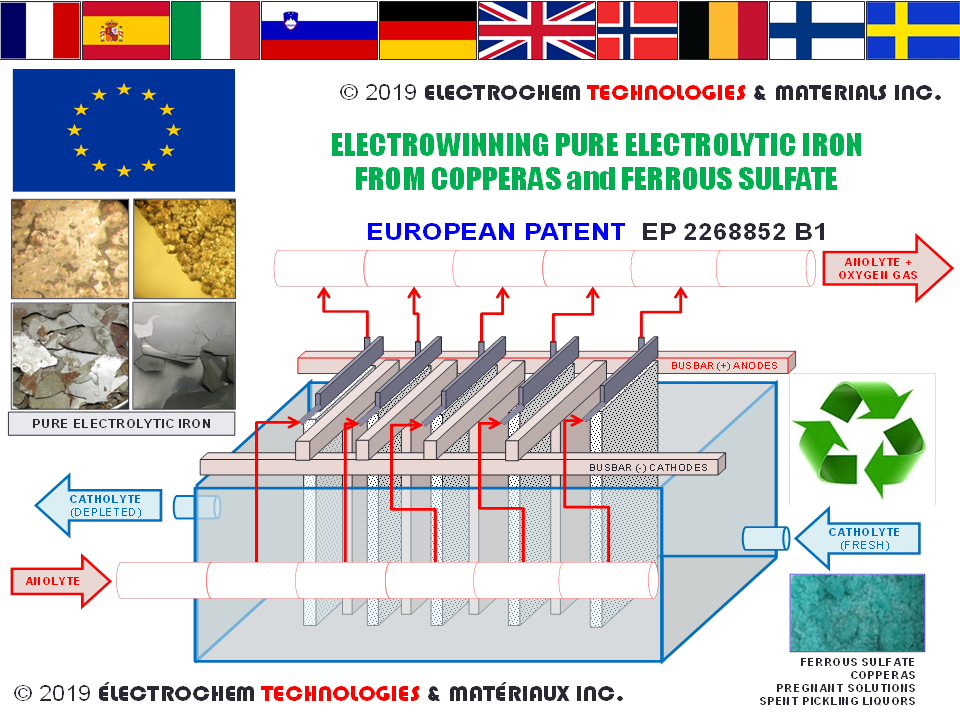 |
September 5th, 2019 - EUROPEAN PATENT GRANTED AND ENFORCED IN FRANCE (FR), ITALY (IT), SPAIN (ES), BELGIUM (BE), GERMANY (DE), GREAT BRITAIN (GB), SLOVENIA (SI), NORWAY (NO), SWEDEN (SE) AND FINLAND (FI) FOR ELECTROWINNING IRON AND IRON-RICH ALLOYS FROM FERROUS SULFATE(S), COPPERAS, MINING WASTES, METALLURGICAL EFFLUENTS, AND SPENT PICKLING LIQUORSMONTREAL, QC – September 5th, 2019 – We are pleased to announce that the European Patent EP 2268852 B1 of entitled Electrochemical process for the recovery of metallic iron and sulfuric acid values from iron-rich sulfate wastes, mining residues, and pickling liquors granted last December 5th, 2018 has been finally validated and granted in 10 countries of the European Union (EU): France (FR), Italy (IT), Spain (ES), Slovenia (SI), Belgium (BE), Germany (DE), the United Kingdom (UK), Norway (NO), Sweden (SE) and Finland (FI) where this disruptive green iron-making technology is the most attractive to be implemented industrially. These ten patents in key EU jurisdictions give ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. exclusivity for the use of this invention in the selected countries within the EU for a period of twenty years following the PCT filing date (April 14th, 2009). This zero-carbon iron making process was successfully applied to copperas (ferrous sulfate heptahydrate) from the titanium process industries, spent pickling liquors (SPL) from metal processing facilities , pregnant leach solutions (PLS) from the metallurgical industries. This novel and disruptive technology produces either pure electrolytic iron or high value iron-rich alloys. The final product is in the form of nodules, thick plates, stripped foils, flakes, or even iron metal powder depending on the operating conditions and the type of electrolyzer design. Consequently, ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. is now well positioned to advance our efforts to commercialize this novel green iron-making technology in the EU with our current industrial partners. |
 |
July 7th, 2019 - PRODUCTION OF VANADIUM REDOX FLOW BATTERY ELECTROLYTE SOLUTIONS TO EXPAND.MONTREAL, QC – July 7th, 2019 – We are pleased to announce that Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. (“Electrochem”) produces at its facilities located in Boucherville, QC, Canada, Vanadium Equimolar Battery Electrolyte Solutions (Vanalyte) used in vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFB). The company proprietary electrochemical process relies on technical grade vanadium pentoxide, concentrated sulfuric acid, de-ionized water and electricity. The vanadium electrolyte does not contain by-products or deleterious impurities as no reducing agents are utilized compared to the conventional chemical route. This results is a fast, robust, and cost affordable production of vanadium electrolyte. Following commercial meetings with vanadium redox flow battery (VRB) manufacturers in North America and overseas, the company is now aiming to expand its production capacity by installing larger modular units to reach the targeted nameplate capacity of 1000L/day in the near future while some customers expressed their strong commercial interest to have access to skid mounted and containerized units for refueling their VRFB systems on-site or to establish regional supply stations. For more information. |
 |
May
23rd, 2019 - ULTRA
POWER SYSTEMS PTY. LTD. EXECUTES THE SECOND PAYMENT TO PURCHASE A
LICENSE FOR THE VANADIUMCORP-ELECTROCHEM PROCESS TECHNOLOGY (VEPT) FOR
AUSTRALIA
|
 |
March 1st,
2019 - NATIONAL ENTRY PHASES FILED IN AUSTRALIA, CANADA, INDIA, THE
UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AND THE REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA FOR
THE VANADIUMCORP-ELECTROCHEM PROCESS TECHNOLOGY (VEPT)
MONTREAL,
QC – March 1st, 2018 – We are pleased to
announce that VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. (“VRB”) and Electrochem Technologies &
Materials Inc. (“Electrochem”) have
jointly filed
internationally for the national entry phases in Australia,
Canada, India, the United States of America, and the Republic of South
Africa of the international patent application entitled: METALLURGICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROCESS FOR RECOVERING VANADIUM AND IRON VALUES FROM
VANADIFEROUS TITANOMAGNETITE AND VANADIFEROUS FEEDSTOCKS.
This patent pending technology ointly owned by VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. and Electrochem Technologies &
Materials Inc. is a novel chemical
process that addresses the recovery of vanadium, iron, titanium and
silica values from a plethora of vanadiferous feedstocks especially
vanadiferous titanomagnetite. The filing of
the National Phase Entry in Australia, South Africa, India and the
Unites States will support future licensing and/or partnership
opportunities in those specific jurisdictions. Subsequent filings are
planned in other key jurisdictions in the coming months. |
 |
February
17th, 2019 - ELECTROCHEM
TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. STARTS COMMERCIAL PRODUCTION IN
CANADA OF ALL-VANADIUM EQUIMOLAR ELECTROLYTE SOLUTION FOR VANADIUM
REDOX FLOW BATTERIES (VRFB)
MONTREAL,
QC – February 17th, 2019 – We
are pleased to announce that Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc.
(“Electrochem”) started
commercial production in Canada of
sulfate based all-vanadium equimolar electrolyte solution following several
months of comprehensive in-house research and experimental development
program regarding the electrochemical preparation
of vanadium redox
flow
battery electrolyte (VRFBE). The production,
which is now performed on demand, utilizes the company proprietary VRFBEX semi-pilot unit while a larger
unit is currently under construction. The research and experimental
development programn addressed key aspects such as testing and
characterizing the electrolyte solution produced (pH, ORP, electrical
conductivity, dynamic viscosity, surface tension, UV-Vis spectral
absorbances, redox potentiometric titration of vanadium species,
voltammetry, free sulfuric acid determination by gas volumetry,
gravimetric analysis), the performances of electrodes (Tafel parameters
at high current densities, Faradaic current efficiency, specific
energy consumption, space time yield, potential drift over time) and
ion exchange membrane materials (area specific impedance (ASI), water
permeability, protons rejection, anion and cation permeabilities, ion
exchange capacity, fooling, thermal and chemical stability, bursting
pressure, swelling), but also assessing and qualifying several
sources of technical grade vanadium pentoxide purchased
directly from established traders and chemical suppliers. Actually,
most vanadium redox flow battery electrolytes available commercially
exhibit extremely low concentration of metallic and non metallic
impuritites. Maintaining such low concentrations requires to use high
purity feedstocks and it is not always justified electrochemically nor
necessarily required for long lasting operating performances.
Electrochem's unique "bottom-up" approach aimed to
produce a low cost all-vanadium equimolar electrolyte solution with
less stringent technical specifications regarding some impurities
thresholds while
establishing an all vanadium electrolyte standard acceptable
commercially to be used in energy storage and power sources such as
vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFB). Moreover,
deleterious impurities especially some reducible metals were removed
efficiently by the cathodic process by carefully selecting the
cathode material and enhancing its
properties by proper surface finishing. Moreover, our knowledge and
manufacture of proprietary electrode
materials and the identification of low
cost membranes materials exhibiting excellent
performances under the harsh operating conditions of slurry
electrolysis allowed us to to reduce significantly the installation
capital expenditure (CAPEX) and the operating cost (OPEX) thus
increasing our profit margin. Samples of balanced
all vanadium equimolar electrolyte solutions were also qualified externally
and in a near future the acquisition and installation of a small
commercial vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) fully equipped stack and
a battery testing system and related cycler will allow us to perform
such testing directly in-house. The batches can also be tailored to
suit customers requirements especially regarding key additives. We
hope that this new commercial activity despite being small can
complement our current commercial production of industrial electrodes,
tantalum, and tungsten fine chemicals. Please do not hesitate to
contact us for technical and/or commercial enquiries: sales@electrochem-technologies.com. |
 |
January
18th, 2019 - ELECTROCHEMICAL
SEMI-PILOT UNIT "VRFBEX" FOR THE SMALL
SCALE COMMERCIAL PRODUCTION OF VANADIUM REDOX FLOW BATTERY ELECTROLYTE
(VRFBE)
MONTREAL,
QC – January 18th, 2019 – We
are pleased to announce that Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc.
(“Electrochem”) has
completed the construction and tested its proprietary semi-pilot electrochemical unit we
called "VRBFEX"
to be used for both qualification purposes and company small
scale commercial production
of vanadium redox
flow
battery electrolyte (VRFBE). The
unit converts technical grade vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) we
purchase on the market as main raw material using the conventional
electrochemical slurry
reduction process. The unit is based on
our PROTOTYPE
II and FLOWPRO
III plate and frame electrolyzer stack designs. Moreover, it
utilizes our proprietary advanced electrode materials (anodes and
cathodes) manufactured to enhance the electrolysis performances especially
the space time yield (Y
in kg.m2.h-1) and to lower the overall specific
energy consumption (em in kWh/kg) using
customized and low cost ion exchange membranes. The
electrolyzer stack exhibits a total electrode surface area
ranging from two square feet (0.186 m2) up to ten square
feet (0.929 m2). The production nameplate
capacity
ranges from 18.9 L per day (5 gallons/day) up to
60L per day (15 gallons/day) of balanced equimolar
all vanadium redox flow battery electrolyte [i.e., 1.6 M V(total), 2.0
M H2SO4 (free) and with a
molar ratio V(IV)/V(III) = 1.0]. This robust and cost
affordable electrochemical unit was initially designed to offer a cost
effective solution for the company commercial production of vanadium
redox flow battery electrolyte in order to
supply targeted customers. A much larger and
compact unit was designed and it is currently under technical
assessment. Finally, using a specifically developped computer program
based on gathered experimental data
from measurements of pH, ORP, electrical conductivity, mass density,
refractive index, and spectral absorbance, we can predict with a good
accurary and reliability the production status
and the final specifications of the equimolar vanadium redox flow
battery electrolyte. Please do not
hesitate to contact us for technical and/or commercial enquiries: sales@electrochem-technologies.com. |
 |
December
10th, 2018 - ULTRA
POWER SYSTEMS PTY. LTD. SIGNS EXCLUSIVE PATENT OPTION AGREEMENT TO
PURCHASE A LICENSE FOR THE VANADIUMCORP-ELECTROCHEM PROCESS TECHNOLOGY
(VEPT) FOR AUSTRALIA
|
 |
December 5th, 2018 - EUROPEAN PATENT GRANTED FOR ELECTROWINNING IRON AND IRON-RICH ALLOYS FROM FERROUS SULFATE COPPERAS, MINING WASTES, METALLURGICAL EFFLUENTS, AND SPENT PICKLING LIQUORSMONTREAL, QC – December 5th, 2018 – We are pleased to announce that the European Patent Office (EPO) has granted the patent EP 2268852 B1 entitled Electrochemical process for the recovery of metallic iron and sulfuric acid values from iron-rich sulfate wastes, mining residues, and pickling liquors. The grant was given and we will now select the countries in the European Union (EU) where the patents will be validated. Once granted these patents in several key EU jurisdictions will give ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. exclusivity for the use of this invention in the selected countries with the EU for a period of twenty years following the PCT filing date (April 14th, 2009). This zero-carbon iron making process was successfully applied to copperas (ferrous sulfate heptahydrate) from the titanium process industries, spent pickling liquors (SPL) from metal processing facilities , pregnant leach solutions (PLS) from the metallurgical industries. This novel and disruptive technology produces either pure electrolytic iron or high value iron-rich alloys containing also Ni, Co, Cr, Mn, Cu, Zn, and V. The final product is in the form of nodules, thick plates, stripped foils, flakes, or even iron metal powder depending on the operating conditions and the type of electrolyzer design. Consequently, ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. is now well positioned to advance our efforts to commercialize this disruptiveh technology worldwide with our current industrial partners. |
 |
October
12th, 2018 - ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS WINNER OF
THE ICIS INNOVATION AWARDS 2018 IN THE CATEGORY BEST INNOVATION BY
A SMALL BUSINESS or MEDIUM SIZE ENTERPRISE (SME)
MONTREAL,
QC – October 12th, 2018 – The ICIS announced today that the
independent judges of the ICIS
INNOVATION AWARDS 2018 selected the
company ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. and
its President François Cardarelli as the winner in the Best
Innovation by a Small or Medium Size Enterprise (SME)
category, sponsored by ExxonMobil
Chemical which highlight the company flagship patented
technology: Electrowinning iron from
copperas: a zero-carbon iron-making process. The chemical industry
and innovation can play a key role in addressing many of today’s
environmental concerns, including global warming, pollution, recycling,
water supply security and nutrition. The Innovation with Best
Innovation by a Small or Medium Size Enterprise (SME) category won
by Electrochem recognizes the implementation of ideas relating to
environmental performance and sustainability into the company’s product
and process innovation. |
 |
August
30th, 2018 - PCT OF THE INTERNATIONAL PATENT APPLICATION WO
2018/1152628 (A1) PUBLISHED BY THE WIPO
MONTREAL,
QC – August 31st, 2018 – The World
Intellectual Property Organization (www.WIPO.int)
has just published the PCT of the International Patent Application WO 2018/152628 (A1) [PDF file (4.5 MB)]
entitled - METALLURGICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROCESS FOR RECOVERING VANADIUM AND IRON VALUES FROM
VANADIFEROUS TITANOMAGNETITE AND VANADIFEROUS FEEDSTOCKS.
This patent is jointly owned by VanadiumCorp
Resource Inc. and Electrochem
Technologies & Materials Inc. and it describes a novel chemical
process that addresses the recovery of vanadium, iron, titanium and
silica values from a plethora of vanadiferous feedstocks such as
vanadiferous titanomagnetite, iron ores and concentrates (magnetite and
hematite), vanadium containing industrial wastes such as BOF-slags and
other industrial by-products also containing vanadium. The process
consists to digest the vanadiferous feedstocks into concentrated
sulfuric acid. Owing to the exothermic sulfation reaction this allows
to operate quasi-autogeneously producing a hard sulfation cake. The
dissolution of the sulfation cake after separating the insoluble
solids yields a concentrated pregnant solution. After reducing
electrochemically the pregnant solution, the reduced liquor is then
subjeced to chilling and crystallization that yields clean crystals
of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas). The process further
comprises removing titanium by hydrolysis from the iron depleted
solution thereby producing a vanadium-bearing pregnant solution. The
further concentration by evaporation and then a sequence of chilling
and crystallization yields vanadyle sulfate to be purified further to
prepare various vanadium chemicals or as key precursor for the
preparation of vanadium electrolyte (VE) used in vanadium redox flow
batteries (VRFB). |
 |
July 24th, 2018 - PILOT UNIT FOR ELECTROWINNING IRON AND IRON-RICH ALLOYS FROM FERROUS SULFATE COPPERAS, MINING WASTES, METALLURGICAL EFFLUENTS, AND SPENT PICKLING LIQUORSMONTREAL, QC – July 13th, 2018 – We recently build another pilot unit for electrowinning electrolytic iron (ca. 1/50 commercial scale) that allows us to perform all the current operation units required by this green electrochemical process (e.g., electrowinning, catholyte conditioning and bath dumying, copperas addition, heat exchangers, gas-liquid separation, solid-liquid separations by gravity settling, cycloning and filtration, etc.). Actually, smaller units were installed in the past at some client sites for demonstration purposes. This improved setup was designed to mimic an industrial electrolyzer operating under actual conditions with various feed materials (copperas, spent acids, pickling liquors, pregnant leach solutions). This in order to support the commercial deployment of the novel technology at client sites that will use either rectangular polymer concrete cells or cylindrical tanks. For this purpose, we have also optimized and manufactured mixed metal oxide anodes with long service life and low oxygen overvoltage and customized framed membranes. Finally, using an in-house program and retrieving the experimental data obtained from the mini-pilot campaigns, we can predict with an excellent accurary and reliability the actual performances of the commercial electrolyzer based on the same feed and operating conditions. Our comprehensive database of electrode materials performances under a plethora of operating conditions and electrolytes properties, that were gathered in the last eight years, is in part responsible for its excellent accuracy and reliability. This innovative approach has convinced the engineering staffs from our existing clients to favor such mini-pilot campaigns precluding expensive large scale tests on-site. |
 |
May 2nd, 2018 - NOTICE OF ALLOWANCE RECEIVED FROM THE EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE FOR THE PATENT APPLICATION ELECTROWINNING IRON AND IRON-RICH ALLOYS FROM FERROUS SULFATE COPPERAS, MINING WASTES, METALLURGICAL EFFLUENTS, AND SPENT PICKLING LIQUORSMONTREAL, QC – May 2nd, 2018 – We are pleased to announce that the European Patent Office (EPO) has issued a notice of allowance for the patent application EP 09730372 A1 entitled Electrochemical process for the recovery of metallic iron and sulfuric acid values from iron-rich sulfate wastes, mining residues, and pickling liquors. The authorization was given for translating the claims and in the coming month we will select the countries in the European Union (EU) where the patents will be granted and we expect patent issuance within usual timeframe. Once granted these several patents will give ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. exclusivity for the use of this invention in the selected countries with the EU for a period of twenty years following the PCT filing date (April 14th, 2009). This zero-carbon iron making process was successfully applied to copperas (ferrous sulfate heptahydrate) from the titanium process industries, spent pickling liquors (SPL) from metal processing facilities , pregnant leach solutions (PLS) from the metallurgical industries. This novel and disruptive technology produces either pure electrolytic iron or high value iron-rich alloys containing also Ni, Co, Cr, Mn, Cu, Zn, and V. The final product is in the form of nodules, thick plates, stripped foils, flakes, or even iron metal powder depending on the operating conditions and the type of electrolyzer design. Consequently, ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. is now well positioned to advance our efforts to commercialize this disruptiveh technology worldwide with our current industrial partners. |
 |
March 29th, 2018 - INDIA PATENT GRANTED FOR ELECTROWINNING IRON AND IRON-RICH ALLOYS AND RECYCLING SULFURIC ACID FROM COPPERAS, MINING WASTES, METALLURGICAL EFFLUENTS, AND SPENT PICKLING LIQUORSMONTREAL, QC – March 29th, 2018 – We are pleased to announce that the patent entitled Electrochemical process for the recovery of metallic iron and sulfuric acid values from iron-rich sulfate wastes, mining residues, and pickling liquors is now granted and enforced in India under the Patent Number 294372. This zero-carbon iron making process was successfully applied to copperas (ferrous sulfate heptahydrate) from the titanium process industries, spent pickling liquors (SPL) from metal processing facilities , pregnant leach solutions (PLS) from the metallurgical industries. This novel and disruptive technology produces either pure electrolytic iron or high value iron-rich alloys containing also Ni, Co, Cr, Mn, Cu, Zn, and V. The final product is in the form of nodules, thick plates, stripped foils, flakes, or even iron metal powder depending on the operating conditions and the type of electrolyzer design. This new patent in our portfolio will give us exclusivity for the use of this invention in India for a period of twenty years following the filing date (October 18, 2010). Consequently, ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. is now well positioned to advance our efforts to commercialize this disruptiveh technology worldwide with our current industrial partners. |
 |
March 15th, 2018 - FERROUS SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE (COPPERAS): A POTENTIAL NEW BENCHMARK FOR PRODUCING PURE ELECTROLYTIC IRON BY ELECTROWINNING AS A GREEN AND ZERO-CARBON IRON MAKING PROCESSMONTREAL, QC – March 12th, 2018 – ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. is please to report that after more of 8 years of intense development both in-house and at client sites worldwide of its patented electrowinning technology (Canadian Patent 2,717,887 C) for producing pure electrolytic iron from ferrous sulfate heptahydrate also known as copperas, the company is closer than ever to establish copperas as a new benchmark for a green and zero-carbon iron making process. Actually, copperas is a well know industrial by-product from the titanium pigment industries with an annual tonnage approaching 8.8 million tonnes globally. Moreover, it is estimated from an internal market review that the metallurgical industries also generate more than 9.5 million tonnes of copperas equivalent annually while the pickling of steel still by-produces about 6.5 million tonnes of copperas equivalent. The electrowinning of copperas not only produces pure electrolyic iron with estimated CAPEX and OPEX that are very attractive compared to the construction of a new smelter facilities but it solves two huge environmental issues: (1) by avoiding the utilization of a carbon reductant and relying on hydro-electricity it prevents the release of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere instead its releases oxygen gas; (2) by recycling existing wastes and effluent streams from the above industries it prevent their final disposal. Finally, using copperas, pure electrolytic iron can be produced in various commercial forms such as flakes, powder, plates, slabs or nodules suitable to be used directly by end-users or used as a feed instead of sponge iron to be pressed or sintered or remelted for the production of high quality steels. |
 |
February 28th, 2018 - VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. and Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. FILED FOR INTERNATIONAL PATENT ADDRESSING THE CHEMICAL AND METALLURGICAL PROCESSING OF VANADIFEROUS TITANOMAGNETITE & OTHER VANADIFEROUS FEEDSTOCKSMONTREAL, QC – February 28th, 2018 – ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. and VANADIUMCORP RESOURCE INC. VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. (TSX-V: “VRB”) are pleased to announce that they have jointly filed for an international patent application with the World International Patent Organization (WIPO) under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) on February 21st, 2018 in order to secure IP rights for the new VanadiumCorp-Electrochem technology worldwide.This new application claims the benefit of priority of the two co-pending US provisional patent applications (62/463,411 and 62/582,060) filed on February 24th, 2017 and November 7th, 2017 with the United States Patent & Trademark Office (USPTO). The technology invented by Dr. Francois Cardarelli addresses the efficient recovery of vanadium compounds including vanadyl sulfate and vanadium pentoxide, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas), titania and silica by-products from vanadiferous feedstocks. The disclosed subject matter of the PCT application is strongly supported by results of metallurgical and chemical trials conducted at Electrochem's facilities located in Boucherville, QC, Canada. The PCT Application is a unified international patent application with 152 participating independent states and countries. With the filing of the PCT Application, the VanadiumCorp Electrochem Process Technology is now protected and once the PCT will be issued patent applications will be filed in selected countries and become patent pending in the chosen national jurisdictions. [For more details please refer to the official news release from VanadiumCorp.] |
 |
January 16th, 2018 - VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. and Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. Sign Partnership AgreementMONTREAL, QC – January 16th, 2018 – ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC is pleased to announce that the company signed a partnership agreement with VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. (TSX-V: “VRB”) further to the memorandum of understanding signed and announced last February 9th, 2017. The partnership expands on successful collaboration that began in 2016 with the objective of commercial demonstration. The new chemical process represents a green and efficient alternative to current polluting and inefficient methods of processing utilized in the vanadium, steel, iron and energy storage industries. The terms of the Partnership Agreement Include:• 50/50 agreement on development and licensing of the patent pending VanadiumCorp-Electrochem chemical technology that allows the dissolution of 95%+ VTM directly into sulfuric acid with the separation of iron values as ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas) along with titania and silica as by-products yielding a vanadyl sulfate solution. • Development partnership targeting North American demonstration, commercialization and scaled production plans relating to secured feedstock supply • Development partnership targeting pilot plant demonstration, commercialization and scaled production applied to VanadiumCorp's 100% owned VTM Resources • Buyout provision [For more details please refer to the official news release from VanadiumCorp.] |
 |
December 19th, 2017 - VANADIUM PRODUCTION TRIALS COMPLETEDMONTREAL, QC – August 08th, 2017 – ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC is pleased to announce the completion of Phase II Vanadium production trials at our facilities located in Boucherville, Quebec. Phase II yielded positive results that demonstrated the industry potential for VanadiumCorp-Electrochem jointly owned and patent pending chemical technology. Phase II resulted in successful processing of a variety of feedstocks ranging from magnetite, residues, slags and calcine that related industries cannot process efficiently or avoid the significant release of greenhouse gases. The Phase II results include: (i) efficient processing of a plethora of feedstocks with 95% of the material being recovered in the case of magnetite; (ii) recovery of vanadium as vanadyl sulfate used a precursor for the preparation of vanadium electrolyte (VE); (iii) demonstration of the full potential of the VanadiumCorp-Electrochem chemical technology for primary production and monetization of waste materials; (iv) detailed mass and energy balances allowing the calculations of specific energy consumptions for the overall chemical and electrochemical integrated processes; (v) titania and silica were recovered as value added byproducts with good marketable values; (vi) excellent reproducibility with similar yields and recoveries of vanadium, iron, titania and silica products from magnetite from various geographical origins; (vi) technical and cost-effective confirmation of Electrochem's exclusive patented technology (Canadian Patent 2,717,887 C) for electrowinning pure electrolytic iron from the ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas) produced; (vii) confirmed industrial potential for the fully integrated CO2 free iron making process for replacing the blast furnace in the iron and steel making industries in global jurisdictions having access to affordable electricity; (viii) trial production reactor with 300kg/month nameplate capacty and related equipment at our facilities in Boucherville. The following products were recovered during the campaign:Vanadyl sulfate hydrates.Ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas). Pure red ferric oxide as an alternate recovery option for plant locations facing high electricity cost. Vanadium oxides and vanadium chemicals. Titania-rich and silica by-products. In 2018, the objectives for Phase III are:◾Piloting the technology at client locations using custom designed units mounted onto a skid ◾Commercial plant in Canada or internationally ◾Global licensing and deployment strategy for the two technologies ◾Continued prototype and pilot testing and evaluation of the robustness of the technologies for the vanadium, steel, oil and energy storage industries inning process. [For more details please refer to the official news release from VanadiumCorp.] |
 |
November
24th,
2017
- SUPPLY OF CESIUM TUNGSTATE SOLUTIONS FOR HEAVY MEDIA AND OTHER
APPLICATIONS
MONTREAL, QC –
November 24th, 2017 – ELECTROCHEM
TECHNOLOGIES
&
MATERIALS INC. is pleased to announce that the company now supplies
cesium tungstate (Cs2WO4) it
produces at
its facilities located in Boucherville, Québec, from tungsten
intermediate products originating from the pyrometallurgical and
chemical treatment of various tantalum and niobium concentrates and
industrial by-products using its patented process (Canadian Patent No. 2,849,787 C). The
product is extensively used by our customers in the following niche
markets for more information (Tungsten
and Tantalum Chemicals).
|
 |
August 08th, 2017 - VANADIUM RECOVERY FROM VANADIFEROUS FEEDSTOCKSMONTREAL, QC – August 08th, 2017 – We are pleased to announce that in partneship with VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. (TSX-V: “VRB”) we have produced vanadium-rich pregnant solutions, vanadium oxides and titania by-products using our jointly owned and patent pending VanadiumCorp-Electrochem Technology. This Phase II campaign is inteded to allow the processing of vanadiferous feedstocks from various vanadium producers and from the iron- and steelmaking industries interested in assessing the significant potential of VanadiumCorp-Electrochem Technology. The planned expansion with additional feedstocks will facilitate scaling-up the VanadiumCorp-Electrochem Technology to reach one metric tonne per month nameplate capacity and include adequat infrastructure such as large reactors to process batches of VTM necessary to fully test the production of vanadium oxides, vanadium electrolyte and electrolytic iron for final qualification by potential end users. The wide spectrum of recoverable products has also expanded in Phase II to include the following: vanadium oxides and chemicals such as vanadyl sulfate, titania and silica by-products, copperas, ferric oxides and electrolytic iron using Electrochem's patented electrowinning process. [For more details please refer to the official news release from VanadiumCorp.]
|
 |
July
24th,
2017
- COMMERCIAL PRODUCTION OF TANTALATES & TUNGSTATES FINE
CHEMICALS
MONTREAL, QC – July
24th, 20176 – ELECTROCHEM
TECHNOLOGIES
&
MATERIALS INC. is pleased to announce that the company reached a
significant milestone by processing at our installations the equivalent
of 950 kilograms of raw materials for the commercial production of
tantalates and tungstates fine chemicals such as cesium
tungstate (Cs2WO4) and potassium hexatantalate (K8Ta6O19)
with high added values. These compounds were
produced at 50-kg per batch using our patented metallurgical
process (Canadian Patent No. 2,849,787 C)
and additional know how developped in-house
in
order to supply the small but increasing number of our clients accross
Canada using these expensive salts in their niche applications.
During the last year, our efforts have focussed on qualifying few and
reliable strategic suppliers of raw materials in North America and
abroad while our existing clients provided us with their helpful
feedback regarding the products purchased. This allowed us to retrofit
some critical steps in our process especially on the removal of
ubiquitous impurities
such traces of niobium and molybdenum. |
 |
June 29th, 2017 - HIGH PURITY IRON PRODUCED FROM LAC DORÉ TITANO-MAGNETITE USING HYDROELECTRICITYMONTREAL, QC – June 29th, 2017 – We are pleased to announce that pure electrolytic iron was recovered directly from vanadiferous titanomagnetite (VTM) concentrate prepared from drill cores from VanadiumCorp’s Lac Doré Vanadium Project. Phase II development of Vanadiumcorp-Electrochem Process technology progesses on schedule: (1) the first large reactor designed with a nameplate capacity of 300 kg/month of VTM was successfully installed at Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. facilities in Boucherville using readily available industrial equipment required for production scale-up. Additional customized items will be installed to accommodate the specificity of the patent pending VanadiumCorp-Electrochem technology. (2) Crystals of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas) were successfully crystallized from the pregnant liquor and allowed the electrowinning of pure electrolytic iron using Electrochem’s patented technology. This represents the first time pure electrolytic iron metal was processed from Lac Dore vanadiferous titanomagnetite using hydroelectricity. This demonstrates the potential of implementing this integrated CO2 free iron making process. (3) In parallel, 5 kg batches of VTM were processed using a gallon-size vessel in order to confirm results obtained during Phase I with a particular attention on the consumption of chemicals, energy and water. So far the results confirmed a specific consumption of sulfuric acid close to stoichiometry and a low water utilization allowing to produce highly concentrated liquors suitable for recovering efficiently iron, vanadium, titanium, and silica products. The energy consumption was kept at a minimum relying on the exothermic character of the chemical reactions involved that will allow an autogenous mode of operation when performed industrially. (4) Once fully operational, the large reactor will allow efficient assessment of the technology robustness and to further optimize its design prior to building additional reactors and equipment as Phase II continues toward a targeted nameplate capacity of 1 tonne per month of VTM. (5) Processing other vanadiferous concentrates and metallurgical by-products supplied from various industrial partners worldwide is also expected to facilitate scale-up to 1 tonne per month capacity and the beginning of Phase III. (6) Consistent yields and recoveries (+95%) remain consistent in Phase II confirming the industrial potential of the new and greener technology that can now be applied to other vanadiferous feedstocks, hematite, vanadium slags from steel making, iron ores, and non-monetized calcine from primary vanadium producers that all containing elevated concentrations of iron which are not currently processed efficiently or at all by existing conventional technologies. Finally, we are currently focussing on the preparation on vanadium chemicals and the vanadium electrolyte (VE) for qualification by end users. .[For more details please refer to the official news release from VanadiumCorp.] |
 |
April 13th, 2017 - VANADIUMCORP-ELECTROCHEM PHASE I COMPLETEDMONTREAL, QC – April 13th, 2017 – We are pleased to announce that together with Vancouver based company, VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. (TSX-V: “VRB”) we have completed Phase I development of Vanadiumcorp-Electrochem Process Technology following several months of extensive test work conducted at Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. facilities in Boucherville, Quebec. This represents a major milestone in advancing towards pilot testing, scheduled to begin after Phase II. Phase I established critical success and optimization through direct recovery performed by hydrometallurgical and chemical processing of vanadiferous titanomagnetite (VTM) concentrate that was extracted, prepared and beneficiated by IOS Services Geoscientifiques Inc. , directly from the VRB's 100% owned Lac Dore Vanadium Project in Chibougamau, Quebec. This confirmed efficient recovery of vanadium and iron values using the jointly owned Vanadiumcorp-Electrochem patent pending technology. Consistent yields and recoveries (+95%) were obtained confirmed the industrial potential of the new and greener technology that can now be applied to other vanadiferous feedstocks containing elevated concentrations of iron which are not currently processed by existing conventional technologies. Specific attention was made during the successive campaigns in Phase I to establish accurate materials and energy balances, to optimize the heat and mass transfer during each operation unit, and to minimize the consumption of chemicals and utilities by recycling the various streams back to the process. Moreover, the main chemical stages were performed using reactors and equipment similar to those used industrially for facilitating the future scale-up. For Phase II, the Vanadiumcorp-Electrochem technology will incorporate Electrochem's globally patented technology for electrowinning to produce high purity electrolytic iron. Scaling the process will require bigger infrastructure such as reactors to process larger batches of VTM for producing vanadium pentoxide, vanadium electrolyte and electrolytic iron for final qualification by potential end users. Phase II will also allow VRB to assess the robustness of the fully integrated technologies by processing other vanadiferous concentrates and metallurgical by-products supplied from various industrial partners worldwide. Based on the success of Phase I, VanadiumCorp and Electrochem are both confident about the disruptive integrated approach having a profound impact for processing vanadium and iron feedstocks in Canada and abroad with an exclusive, environmentally friendly technology developed in Quebec, Canada.[For more details please refer to the official news release from VanadiumCorp.] |
 |
February 28th, 2017 - New Technology for Recovering Iron and Vanadium from Vanadiferous TitanomagnetiteMONTREAL, QC – February 28th, 2017 – We are pleased to announce that Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. has applied jointly with Vancouver based company, VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. (TSX-V: “VRB”) for a US provisional patent application (US 62/463,411) for a combined metallurgical and chemical process following the successful test work commenced at our facilities in Boucherville. The testing campaign commenced in 2016 yielded high recoveries of both iron and vanadium values from a vanadiferous titanomagnetite concentrate that was extracted, prepared and beneficiated by IOS Geoscientifiques Inc. (Chicoutimi, QC) from the VanadiumCorp 100% owned Lac Dore Vanadium Project. Conventional pyrometallurgical processes utilize either direct soda ash roasting of the magnetite followed by water leaching, or the arc smelting and slagging of the magnetite followed by soda ash roasting of the vanadium-rich slag. Smelting or roasting is capital intensive with high operating costs, technical risks and significant emissions of greenhouse gases that pose serious environmental issues. Hydrometallurgical processes for the extraction of vanadium have been proposed in the last decade as a lower cost alternative in replacement of the conventional processes but they fail to produce an iron co-product. The Vanadiumcorp-Electrochem Technology addresses these key issues and allows the full recovery of vanadium for the production of either a vanadium electrolyte (VE) or a vanadium chemicals used for preparing vanadium battery electrolyte as well as the concurrent production of a high quality and competitive iron co-product. [For more details please refer to the official news release from VanadiumCorp.] |
 |
February 9th, 2017 - NON-BINDING memorandum of understanding (MoU) SIGNED WITH VANADIUMCORP RESOURCES INC.MONTREAL, QC – February 7th, 2017 – We are pleased to announce that we have signed a non-binding memorandum of understanding “MOU” with Vancouver based company, VanadiumCorp Resource Inc. (TSX-V: “VRB”) to collaborate on metallurgical and electrochemical technologies to produce vanadium electrolyte (VE) directly from vanadiferous titaniferous magnetite (VTM)) concentrate. The non-binding MOU will allow the two companies to collaborate on a number of key strategic initiatives including: (1) the development for the production of vanadium-rich pregnant solution as precursor for the VE and other specialty high purity vanadium materials; (2) the development and commercialization of efficient and environmentally friendly metallurgical and electrochemical processing technologies including the simultaneous removal of contaminant metals and the concurrent regeneration of chemicals; and finally (3) to pursue reasonable efforts to enter into a definitive agreement within 12 months from the effective date of signing for the non-binding MOU. [For more details please refer to the official news release from VanadiumCorp.] |
 |
November
24th,
2016
- SMALL SCALE PRODUCTION OF TANTALUM, NIOBIUM & TUNGSTEN FINE
CHEMICALS FOR SUPPLYING NICHE MARKETS
MONTREAL, QC –
November 24th, 2016 – ELECTROCHEM
TECHNOLOGIES
&
MATERIALS INC. has started the small scale production of tantalum,
niobium and tungsten fine chemicals.
These compounds are produced on-demand from tantalum, niobium and
tungsten by-products and concentrates using our patented pyro- and
hydrometallurgical process (Canadian Patent No. 2,849,787 C). Among
the products sold are: sodium
hexaniobiate (Na8Nba6O19), sodium
hexatantalate (Na8Ta6O19),
potassium hexatantalate (K8Ta6O19),
tantalum pentoxide (technical), niobium pentoxide (technical),
alkali-metals ortho-tungstates (M2WO4),
metatungstates M6[H2W12O40] and
heteropolytungstates Mx[EW12O40]
with M = Li,
Na, K, Cs and E = Si,
and P. |
 |
September
2nd,
2016 -
PYROMETALLURGICAL & HYDROMETALLURGICAL PROCESSING OF VANADIUM
FEEDSTOCK's
MONTREAL, QC –
September 2nd, 2016 – We
are pleased to announce that we have completed last summer a
testing campaign for
the processing of vanadium rich feedstocks from various origins
such as vanadium-rich slag, vanadiferous titanomagnetite, and
vanadium-rich residues.
Electrochem Technologies & Materials Inc. was selected because our
strong know-how in molten salts and high temperature alkaline
processing capabilities. The campaign consisted first
to
perform the
pyrometallurgical treatment of 25-kg batches of raw materials by soda
ash roasting, alkaline roasting and salt roasting using
our 12-kW kiln.
The roasted or sintered material underwent hydrometallurgical operation
units such as alkaline and acid leaching using counter
current cascade leaching reactors
and producing 75 liters per batch of pregnant
leach solution (PLS).
Afterwards, vanadium was precipitated from
the PLS either
as ammonium metavanadate (NH4VO3) or hydrated
vanadium pentoxide (V2O5.250H2O).
Finally at the end of the campaign, our patented electrowinning
technology was used to recover either metallic iron or an iron-vanadium
deposit from the sulfate based pregnant leach solutions while
regenerating concentrated sulfuric acid to be reused back in the
process. This campaign was to some extent in line with the
expertise that was developped in-house over the years by our
company for the metallurgical and chemical processing of
refractory metals of group VB(5) (V, Nb, Ta) and group VIB(6) (Cr, Mo,
W). |
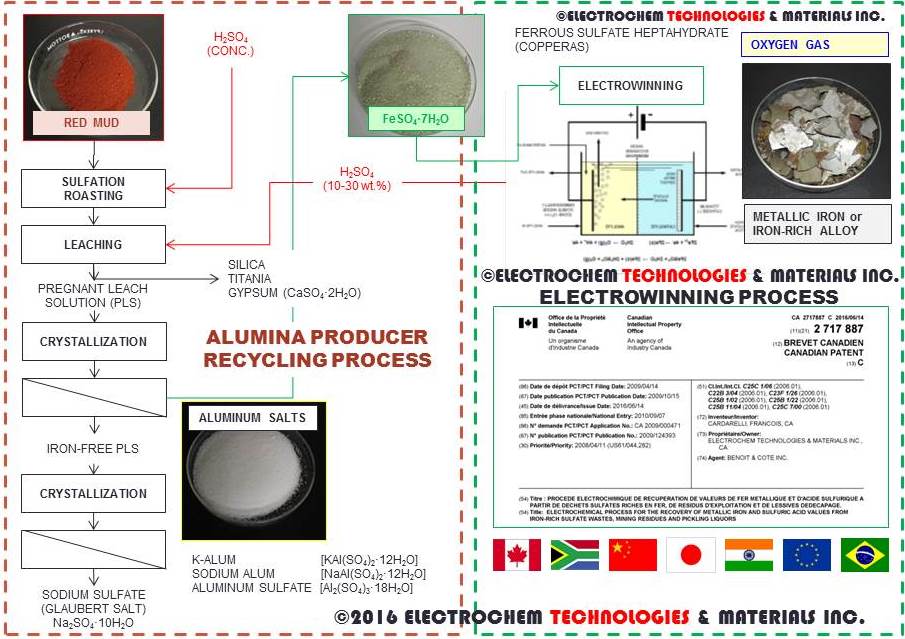 |
July
4th,
2016 -
Recycling red mud by sulfation roasting & electrowinning of iron
MONTREAL, QC – July
4th, 2016 – We
are pleased to announce that we have produced metallic iron and
iron-rich alloy using our patented electrowinning technology from both
ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (copperas) and pregnant leach solutions
(PLS) obtained during the recycling of red mud by sulfation
roasting (i.e., sulfation
baking).
The process under
scrutiny by some alumina producers
consists to react concentrated sulfuric acid with red mud. The aim is
to recover various aluminum by-products (Na-alum, K-alum, aluminum
sulfate) and perform the neutralization and dewatering while yielding
gypsum and sodium sulfate. However, the elevate concentration of ferric
iron along with traces of chromium, vanadium, manganese, zinc, and
nickel in the waste end-up almost entirely in the pregnant
leach solution (PLS) and they must be removed prior to
recover aluminum salts. Two options were tested: first the
electrowinning was performed directly
on
the PLS yielding an
iron-rich alloy containing traces of Mn, Cr, Zn, Ni,
and V while
the second option consisted to electrolyze a concentrated solution
of copperas by-produced after reduction and crystallization from
the PLS producing metallic
iron
By adjusting the proper pH, the colloidal silica, gypsum, and titania
in the PLS migrated towards the cathode ending trapped inside the
deposit hence they were not impacting adversely the performances of the
anion exchange membranes. Based on the excellent space time yield and
low specific energy consumption, we are confident that combining
sulfation-roasting and iron electrowinning could represent a possible
route for neutralizing, dewatering, recycling and valorizing red mud
for geographical locations having access to concentrated sulfuric acid
(e.g., nearby smelters) and affordable electricity (e.g., hydro,
nuclear). From an environmental standpoint, our electrowinning process
also recycles concurrently the sulfuric acid and generate oxygen gas
with a very low carbon foot print when compared to the thermal roasting
route. The samples of PLS and copperas supplied originated from given
red mud chemistries and they are not necessarily representative of all
landfills. Therefore, additional test work will be required to confirm
the industrial applicability of such fully integrated process. As our patent technology is now granted
and pending in several jurisdictions (Canada, China, Japan, South
Africa, European Union, Brazil, and India) where red mud represents a
serious environmental issue, we are in a favorable position to
investigate this synergistic approach with other alumina refiners. |
 |
May 21st, 2016 - PATENTS GRANTED FOR ELECTROWINNING IRON & IRON-RICH ALLOYS & RECYCLING SULFURIC ACID FROM COPPERAS, MINING WASTES, & METALLURGICAL EFFLUENTS, & SPENT PICKLING LIQUORSMONTREAL, QC – May 21st, 2016 – We are pleased to announce that the patent entitled Electrochemical process for the recovery of metallic iron and sulfuric acid values from iron-rich sulfate wastes, mining residues, and pickling liquors is now granted and enforced for twenty years in several jurisdictions (Canada, China, Japan, South Africa) while it is pending approval in the European Union (EU), Brazil, and India . The technology was successfully applied to copperas (ferrous sulfate heptahydrate) from the titanium process industries, spent pickling liquors (SPL) from metal processing facilities , pregnant leach solutions (PLS) from the metallurgical industries, and also recently to acid mine drainage (AMD) from mining sites. This versatile technology produces either pure electrolytic iron or high value iron-rich alloys containing also Ni, Co, Cr, Mn, Cu, Zn, and V. The final product is in the form of stripped foils, flakes, or even powder depending on the operating conditions and the type of electrolyzer design. The total metals concentration in the feed solution ranged from few grams per liter as in acid mine drainage (AMD) up to hundred of grams per liter as with make-up copperas solutions. The process is also robust as it withstand suspended matter such as colloidal silica, titania, and particulate graphite (smut). |
 |
April 28th, 2016 - SEPARATION BY ION EXCHANGE OF TERBIUM, EUROPIUM, GADOLINIUM, YTTRIUM, & LANTHANUM FROM RECYCLED FLUORESCENT LAMPSMONTREAL, QC – April 28th, 2016 – We are pleased to announce that ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. has started a third prototype (50 L/day) campaign for the separation of the five rare earth elements (Y, La, Eu, Gd, and Tb) from a concentrated solution obtained from the processing of phosphors powder using our patented technology. The separation is performed by ion exchange (IX) resins with pH-gradient elution. The target is to achieve faster separation of yttrium, europium, gadolinium and terbium with the same resolutions obtained previously. The main objective of the campaign is to determine the best eluents chemistries, to increase the flow rate, to select the best IX resin formulations. New samples of pure rare earth compounds will be send for qualification to end users soon. From this third extensive campaign, we expect to refine previous operating costs (OPEX) and CAPEX related to a future commercial scale operation. Actually, in the case of only four or five lanthanides to be separated without major contaminants and because of the small scale required for the recycling of phosphors powders, ion exchange is actually a very competitive separation technique, beside it is proven commercially. Finally, the degradation of the IX resin is very small under the mild operating conditions and hence the replacement costs for the resins does not impact significantly the OPEX. The next step will be to build a larger mobile separation unit in order to process 1000 liters of concentrated solution per day. The unit that will be mounted on skid will be installed at our partner plant site. |
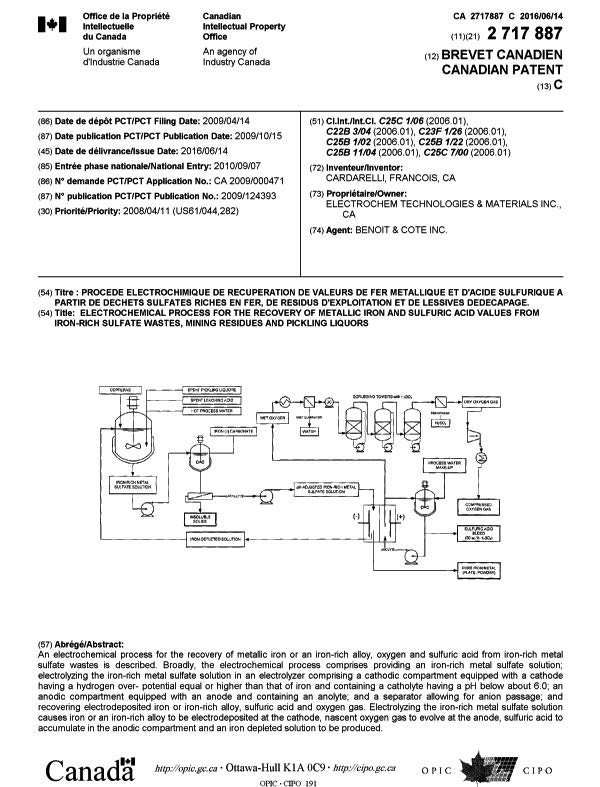 |
March 17th, 2016 - NOTICE OF ALLOWANCE FOR THE CANADIAN PATENT APPLICATION FOR ELECTROWINNING IRON & IRON-RICH ALLOYS & RECYCLING SULFURIC ACID FROM COPPERAS, MINING WASTES, & SPENT PICKLING LIQUORSMONTREAL, QC – March 17th, 2016 – We are pleased to announce that the Canadian Intellectual Property Office (CIPO) has issued a notice of allowance for the patent application No. 2,717,887, entitled Electrochemical process for the recovery of metallic iron and sulfuric acid values from iron-rich sulfate wastes, mining residues, and pickling liquors. The final fees were paid and we expect patent issuance within CIPO's usual timeframe of 9 to 12 weeks. This new patent win our portfolio will give us exclusivity for the use of this invention in Canada for a period of twenty years following the filing date (April 14th, 2009). Consequently, ELECTROCHEM is now well positioned to advance our efforts to commercialize this breakthrough technology with our current industrial partners. |
 |
February
25th,
2016
- PURE TANTALUM PENTOXIDE & SODIUM METATUNGSTATE FOR QUALIFICATION
BY END USERS
MONTREAL, QC –
February 24th, 2016 – ELECTROCHEM
TECHNOLOGIES
&
MATERIALS INC. has shipped a second batch
of tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5) and sodium
metatungstate [Na6(H2W12O40)] to
selected end users for
testing and qualification. These compounds were
produced at the semi-pilot scale from tantalum and tungsten by-products
and concentrates using our patented pyro- and hydrometallurgical process (Canadian Patent No. 2,849,787 C). Initially,
blue tungsten trioxide was prepared but it was decided to produce
sodium metatungstate instead to address niche markets such as heavy
media separation among other uses. A small
portion of the tantalum pentoxide produced was utilized last January
for preparing tantalum crystals and tantalum metal powder by
electrowinning in molten salt electrolytes. This latter option could
allow the company to expand the range of refractory metal services and
products offered. |
 |
February
9th,
2016
- ELECTROCHEM GRANTED PATENT FOR RECYCLING RARE EARTHS FROM FLUORESCENT
LAMPS IN CANADA
MONTREAL, QC –
February 9th, 2016 – We
are pleased to announce that the Canadian
Intellectual Property Office (CIPO) has granted the Canadian patent No.
2,878,486, entitled PROCESS
FOR RECOVERING RARE EARTH OXIDES FROM PHOSPHORS, FLUORESCENT LAMPS AND
LIGHT BULBS, CATHODE RAY TUBES AND OTHER INDUSTRIAL WASTES. This
new patent in our portfolio will give ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES &
MATERIALS INC. exclusivity for the use of this invention in Canada
for a period of twenty years following the filing date
(November 08th, 2013).
Consequently, ELECTROCHEM
is now
well positioned to advance our efforts to commercialize this
breakthrough technology with our current industrial partners and
lamps recycler who did assess the entire process at the semi-pilot
scale in 2014 and 2015 with a nominal production rate of 50 kg/day.
These results have shown an
OPEX as low as $3.00 per kilogram of phosphors powder processed
including retorting. |
 |
October
2015
- ELECTROCHEMICAL REMEDIATION BY ELECTROCOAGULATION OF SPENT LIQUORS
FROM HARD CHROMIUM PLATING
MONTREAL, QC –
October 09th, 2015 –
Several prototype tests regarding the electrochemical treatment
and remediation of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] in spent acidic baths
from hard chromium plating were performed using a protype electrolyzer
of 50 liters nominal capacity and 1.0 m2 of total electrodes
active surface area and a compact flow-through plate electrolyzer both
capable to operate at 4 gallons per minute. Among the electrochemical
remediation techniques used both electrocoagulation and
electroderuction were tested concurrently. The impact of the chemical
composition of various sacrificial metallic anodes was investigated
thoroughly to select the most efficient commercial grade. Actually,
some plating additives especially fluoride anions affect the
passivation behavior of the sacrificial anode used. On the other hand,
various commercial cathode materials were investigated in
order to achieve the highest reducing power in order to lower the
residence time and perform the highest removal rate of Cr(VI). |
 |
September
2015
- HEAVY DUTY MIXED METAL OXIDES (MMO) ANODES & CHEMICALLY ACTIVATED
TITANIUM CATHODES FOR TREATING CONTAMINATED WATERS & LIQUID
EFFLUENTS
MONTREAL, QC –
September 15th, 2015 –
Heavy duty mixed metal oxides (MMO) anodes together with chemically
activated titanium cathodes were fabricated to suit the needs of a
Canadian customer who is deeply involved in the electrochemical
remediation of liquid effluents, and waste waters. The heavy duty
electro-catalytic coating combined with a compact cylindrical design
allowed our client to reduced considerably the foot print of its
flow-through electrolyzers. It was possible to operate under high
current densities favorable for
generating highly oxidizing species and fast pumping
rates improving the space time yield. Moreover, the typical bundle
assemblies created highly turbulent hydraulic conditions suitable for
preventing the formation of tenacious scale at the cathodes. Finally,
as quick installation and desinstallationg was of paramount importance
for daily maintenance, a
particular mode of connecting the anodes to the busbars was achieved. |
 |
May
2015
- ELECTROCHEM GRANTED PATENT FOR UPGRADING TANTALUM & NIOBIUM
OXIDES IN CANADA
MONTREAL, QC – May
5th, 2015 – We
are pleased to announce that the Canadian
Intellectual Property Office (CIPO) has granted the Canadian patent
No. 2,849,787, entitled PROCESS
FOR UPGRADING TANTALUM AND NIOBIUM ORES AND CONCENTRATES WITH THE
RECOVERY OF MANGANESE AND RARE EARTHS OXIDES. This new patent in
our portfolio will give ELECTROCHEM TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS
INC. exclusivity for the use of this invention in Canada for a
period of twenty years following the filing date (September 24th,
2012). Consequently, ELECTROCHEM
is now
well positioned to advance our efforts to commercialize this
breakthrough technology with our current industrial partners who did
assess the entire process at the semi-pilot scale in 2014. |
 |
August
2014 - HIGH TEMPERATURE PROTOTYPE ELECTROLYZERS FOR ELECTROWINNING
REFRACTORY METALS, RARE EARTH METALS, AND PLATINUM GROUP METALS (PGMs)
FROM MOLTEN SALT ELECTROLYTES (MSEs)
MONTREAL, QC –
August 21st, 2014 – Following
the request made by business partners to integrate vertically our
patented technologies in order to suit their needs, ELECTROCHEM
TECHNOLOGIES & MATERIALS INC. has just completed the installation
and commissioning of high temperature molten salt electrolyzers of
prototype scale denoted GENERATION I. These versatile prototypes
are used to perform electro-deposition and/or electrowinning of
refractory metals such as vanadium (V), niobium (Nb), tantalum (Ta),
molybdenum (Mo), and tungsten (W), rare earth metals such as neodymium
(Nd), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd) and terbium (Tb), or their alloys
(Nd2Fe14B).
They are also used to recover platinum group metals (PGMs) especially
iridium (Ir) and ruthenium (Ru) from industrial wastes such as residues
from the manufacturing of mixed metal oxides (MMO) anodes or clients
refurbished anodes and spent coating. The high temperature prototype
electrolytic cells were designed to
withstand the wide operating temperatures ranging from 450ºC until 1200ºC and
hence they were constructed
of heat- and corrosion-resistant metals and alloys. The
current GENERATION I prototypes exhibit a maximum production capacity
of 5 kg per day with external heat provided by a 5.5 kW electric
furnace capable to operate 24/7 without interruption. A larger size
electrolyzer denoted GENERATION II is under development with a targeted
production capacity of 25 kg per day. Once the best performances (e.g.,
faradaic current efficiency, hourly and space time yields, and specific
energy consumption) together with operating conditions (e.g.,
temperature, pressure, type of inert atmosphere, molten salt
composition, electro-deposited metal form (ingot, powder, dendrites,
coating), and purity) will be optimized for each client's project, we
expect that a large pilot molten salt electrolyzer will be installed
on-site at our client's facilities. |
 |
June
2014 - A PROCESS THAT RECYCLES RARE EARTH ELEMENTS FROM "URBAN MINING"
|
 |
May
2014 - PCT OF THE INTERNATIONAL PATENT APPLICATION WO 2014/071510 (A1)
PUBLISHED BY THE WIPO
MONTREAL, QC – May 15th, 2014 – The World Intellectual Property
Organization (www.WIPO.int) has just
published the PCT of the International Patent Application WO 2014/071510 (A1) [PDF file (3 MB)]
entitled - PROCESS FOR RECOVERING RARE EARTH OXIDES FROM
PHOSPHORS, FLUORESCENT LAMPS AND LIGHT BULBS, CATHODE RAY TUBES AND
OTHER INDUSTRIAL WASTES. -This novel process addresses the recovery of rare earths
oxides from phosphor dusts, fluorescent lamps and light bulbs, cathode
ray tubes and other industrial wastes containing rare earths elements
in the form of halophosphates, tri-band phosphors and other fluorescent
materials. The process consists: (1) to submit the wastes or spent
materials to either caustic fusion or hot alkaline leaching; (2) to
perform the hot alkaline leaching of the solidified melt to produce
insoluble solid residues and a barren alkaline leaching solution; (3)
To recover the tri-basic sodium phosphate by crystallization from the barren solution; (4) to
oven-dry or calcine the insoluble solid residues; (5) to perform the
hot acid leaching of the oven-dried or calcined solids; (6) to recover
the cerium (IV) oxide from insoluble solids; (7) to reduce the
cerium-free solution, precipitate, acid leach, precipitate, calcine and
recover the europium (III) oxide; (8) to precipitate the remaining rare
earths as oxalates; (9) to calcine the rare earths oxalates and
dissolve the rare earths oxides in acid; (10) to separate the yttrium,
gadolinium, terbium and erbium by ion exchange (IX) or solvent
extraction (SX); (11) to precipitate and calcine the pure oxalates
to yield pure yttrium (III) oxide, gadolinium (III) oxide, terbium
(III, IV) oxides, and erbium (III) oxide; (12) Finally, to regenerate
and recycle the spent alkaline solution after causticization with
calcium oxide or hydroxide. |
 |
March
2014
- ELECTROCHEMICAL REMEDIATION OF LIQUIDS EFFLUENTS & AGRICULTURAL
WASTES
MONTREAL, QC –
March 24th, 2014 –
Several tests regarding the electrochemical treatment and
remediation of various liquid effluents (e.g., landfill leachate,
ammonia and urea containing waters, AMD) and also agricultural wastes
(e.g., hog manure) were performed in QC with several customers directly
on-site with a custom made protype electrolyzer with 50 liters nominal
capacity and 0.5 m2 of total electrodes active surface area.
At one site, the prototype tests was followed by a one-week piloting
campaign using an electrolyzer of 1.5 cubic metersand with 15 square
meters of electrode surface area. Among the electrochemical remediation
techniques used both electrocoagulation and electroflottation were used
concurrently when large amount of suspended matter and/or heavy metals
(e.g., Cu, Ni, Pb, et.) were present while electro-oxidation with
custom MMO formulation was used to degrade organic pollutants. |
 |
June
2013 - A CLEANER, SAFER WAY TO OBTAIN TANTALUM & NIOBIUM
NEW
YORK CITY, NY – June
1st, 2013 – The
American trade magazine CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (www.che.com) has just published its
June 2013 issue including a press release describing the novel
metallurgical process and entitled - A cleaner, safer way to obtain
tantalum and niobium - written by Gerald Parkinson [PDF
File (294 KB)]. The article is published in the CHEMENTATOR section on page 14. |
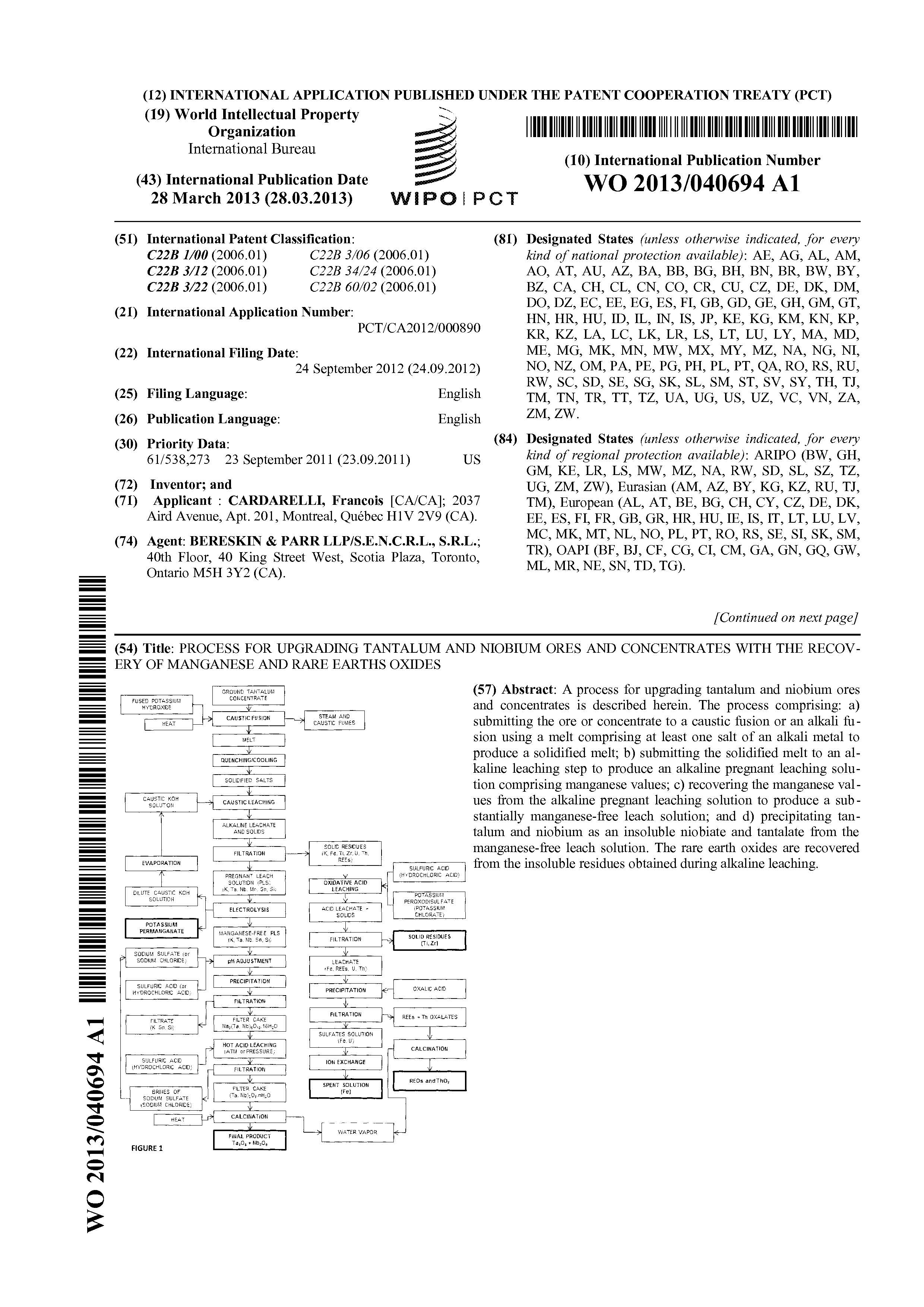 |
March
2013 - PCT OF THE INTERNATIONAL PATENT APPLICATION WO 2013/040694 (A1)
PUBLISHED BY THE WIPO
MONTREAL,
QC – March 29th, 2013 – The
World Intellectual Property Organization (www.WIPO.int)
has just published the PCT of the International Patent Application WO 2013/040694 (A1) [PDF
file
(3 MB)] entitled - Process for
upgrading tantalum and niobium ores and concentrates with the recovery
of manganese and rare earths oxides. - Process for upgrading
tantalum and niobium ores and concentrates is described herein. The
process comprising: a) submitting the ore or concentrate to a caustic
fusion or an alkali fusion using a melt comprising at least one salt of
an alkali metal to produce a solidified melt; b) submitting the
solidified melt to an alkaline leaching step to produce an alkaline
pregnant leaching solution comprising manganese values; c) recovering
the manganese values from the alkaline pregnant leaching solution to
produce a substantially manganese-free leach solution; and d)
precipitating tantalum and niobium as an insoluble sodium niobiate and
tantalate from the manganese-free leach solution. Acid leaching the
sodium niobiate and tantalate to yield a mixture of pure niobium and
tantalum oxides. The rare earth oxides are recovered from the insoluble
residues obtained during alkaline leaching. |
 |
June
2010 - ELECTROCHEMISTRY REGENERATES SULFURIC ACID AND RECOVERS IRON
METAL FROM INDUSTRIAL WASTES
NEW
YORK CITY, NY – June
1st, 2010 – The
American trade magazine CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (www.che.com) has just published its
June 2010 issue including a press release describing the novel
electrochemical technology entitled - Electrochemistry
regenerates H2SO4 and recovers iron from
industrial wastes. - written by Gerald Parkinson. The article
is published in the CHEMENTATOR
section on page 11 [PDF
file (296 KB)]. |
 |
October
2009 - PCT OF THE INTERNATIONAL PATENT APPLICATION WO 2009/124393 (A1)
PUBLISHED BY THE WIPO
MONTREAL,
QC – October 15th, 2009 – The
World Intellectual Property Organization (www.WIPO.int)
has just published the PCT of the International Patent Application WO 2009/124393 (A1) [PDF
file
(2 MB)] entitled - Electrochemical
process for the recovery of metallic iron and sulfuric acid values from
iron-rich sulfate wastes, mining residues, and pickling liquors.
The patent describes a novel electrochemical technology for recovering
metallic iron and concurrently regenerating sulfuric acid from
iron-rich sulfate wastes, such as ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4.7H2O),
also called copperas in the trade, currently by-produced from the
titanium white pigment industry, spent pickling liquors (SPLs)
originating from iron and steel making plants, and finally pregnant
leach solutions (PLS) generated during the acid leaching of ores and
concentrates at various minerals and metals processing plants.
Moreover, the international patent treaty examiner has acknowledged, in
the preliminary report, that the claims of the invention are new,
inventive and that they have a utility. These three criteria are
essential to the patentability of this novel electrochemical process.
This report represents a first and significant milestone in the process
of obtaining patent rights in connection with this novel recycling
technology.
|